
It is divided into two separate accounts common stock and preferred stock. Since the balance sheet amounts reflect the cost and matching principles, a corporation’s book value is not the same amount as its market value. For example, the most successful brand names balance sheet and logos of a consumer products company may have been developed in-house. Since they were not purchased, their high market values are not included in the corporation’s assets. Other long-term assets may have appreciated in value while the accountant was depreciating them. Therefore, they may appear on the balance sheet at a small fraction of their fair market value.
#2 – Retained Earnings

A high number suggests that a company may be able to grow its earnings over time by reinvesting them back into the business, though this is not guaranteed. Below is an overview of return on equity including how to calculate and use it. For example, if a company takes on a bank loan to be paid off in 5 years, this account will include the portion of that loan due in the next year. This account may or may not be lumped together with the above account, Current Debt. While they may seem similar, the current portion of long-term debt is specifically the portion due within this year of a piece of debt that has a maturity of more than one year. In recent years, more companies have been increasingly inclined to participate in share buyback programs, rather than issuing dividends.
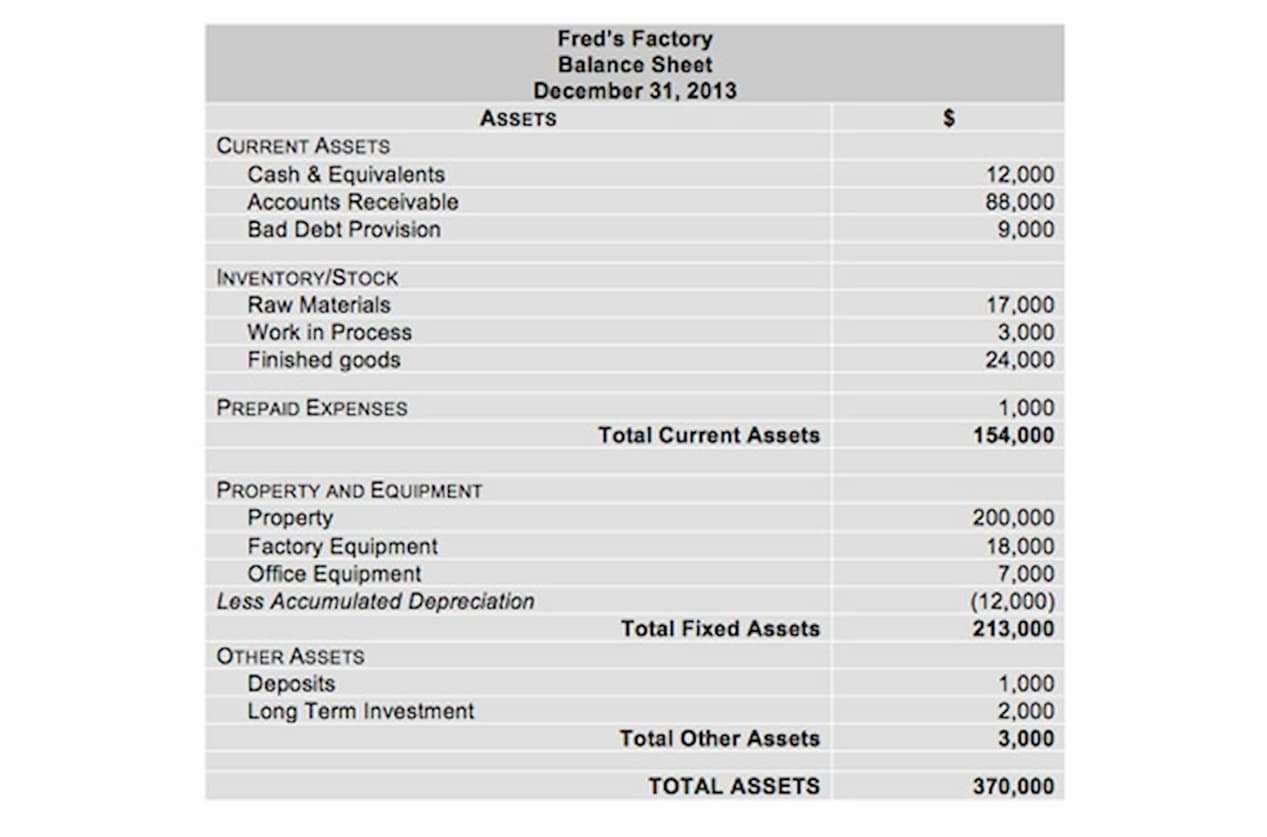
Retained Earnings (or Accumulated Deficit)
The total book value of the preferred stock is the book value per share times the total number of preferred shares outstanding. If the book value per share https://daktarpoint.com/16-best-indianapolis-in-accountants-2/ of preferred stock is $130 and there are 1,000 shares of the preferred stock outstanding, then the total book value of the preferred stock is $130,000. To comply with state regulations, the par value of preferred stock is recorded in its own paid-in capital account Preferred Stock. If the corporation receives more than the par amount, the amount greater than par will be recorded in another account such as Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par – Preferred Stock. For example, if one share of 9% preferred stock having a par value of $100 is sold for $101, the following entry will be made. If the dividend percentage on the preferred stock is close to the rate demanded by the financial markets, the preferred stock will sell at a price that is close to its par value.

Accounting For Stockholders’ Equity
Before making any investment, you’ll want to perform the proper analysis or find an advisor who can help you make those decisions. The simplest and quickest method of calculating stockholders’ equity is by using the basic accounting equation. A current liability account that reports the amounts of cash dividends that have been declared by the board of directors but not yet distributed to the stockholders. The date that determines which stockholders are entitled to receive a corporation’s declared dividend. Insurance Expense, Wages Expense, Advertising Expense, Interest Expense are expenses matched with the period of time in the heading of the income statement.

In other words, they prefer to have the price of a share trading between $40 and $50 per share. If the market price of the stock rises to $80 per share, the board statement of stockholders equity of directors can move the market price of the stock back into the range of $40 to $50 per share through a 2-for-1 stock split. The common stockholder has an ownership interest in the corporation; it is not a creditor or lender.
- In 2021, the share repurchases are assumed to be $5,000, which will be subtracted from the beginning balance.
- An example of a stockholders’ equity is if a company has 300 million in assets and 200 million in liabilities, then the total stockholder’s equity is 100 million.
- The stockholders’ equity concept is important for judging the amount of funds retained within a business.
- Companies might hold onto these shares for various reasons, like decreasing the number of shares in circulation, supporting the share value or using them for employee compensation.
- However, some states allow corporations to issue shares with no par value.
- While the asset value is normally more than the company’s liabilities, there can be instances where the figures reflect an opposite scenario.